Spokes ABC
A
Airplanes
Airplanes were fitted with spoked wheels up into the 20s.


Air pressure
Incorrect air pressure is the cause of most of the tyre damage.
Artillery wheels
Early cars were often equipped with steel-reinforced, wooden spoked wheels like carriages. These so-called artillery wheels usually have eight to twelve spokes per wheel. Initially, the spokes were fixed to the hub. This was impractical, because changing the tyre had to be done on the vehicle, which meant a great deal of hassle to fix a broken wheel. People could only make do with removable rims and carried along one or more with mounted tyres as a replacement.
Axial angle
The axial angle on a spoked wheel refers to the course of the spokes from the inside of the rim to the outside of the hub.
Axial forces
Axial forces occur mainly in the automobiles and motorcycle sidecars. It refers to lateral forces.
B
Balancing
Wheel balancing can be either dynamic or static. Static balancing is used for a variety of two-wheeled vehicles, while all car wheels are balanced dynamically.
- In static unbalance, the unbalance has displaced evenly in the middle of the wheel, parallel to the axis of rotation. This makes one half of the wheel heavier than the other, which makes the wheel jump during rotation.
- Dynamic imbalance can be measured only in rotation. The unbalance is unevenly distributed on both sides of the wheel outside the middle of the wheel. This results in a wobbling movement when the wheel rotates.
Bead
The bead forms the connection to the rim. Steel wires (bead core) embedded in the rubber make the bead stable. The ends of the carcass are placed around the bead. This gives the tyre the desired stiffness in the bead area.
Bend angle
The correct bend angle is necessary to ensure that the spokes are as straight as possible from the hub to the rim. If the bend angle is not right the spoke may flex. Crucial here is the hub-related design with flange widths and flange angles. Typically, inner spokes and outer spokes are required. Inner spokes are introduced from the outside through the holes of the flange of the hub and have an angle of approx. 95°. Outer spokes are usually around 85° and are introduced from the inside through the holes of the flange of the hub.
C
Carcass
The carcass provides the strength of the tyre and also gives the tyre its shape. One or more layers of nylon, rayon, or Kevlar are used as material.
Central lock
In 1905, the company Rudge created a way to allow the complete wheel assembly/wheel removal as a spoke wheel mounting with a central screw. In addition to the classics from the 20s and 30s (Mercedes, Maybach, Jaguar and Horch), this design increasingly became a characteristic of many hiqh-quality sports cars like Aston Martin, Maserati, Iso, MG, Morgan, Austin–Healy and more right into the 1960s. In the 1920s and 1930s, it was such as fashion to hide the wheels under a metal cover that was secured with the same lock that held the wheel in place.

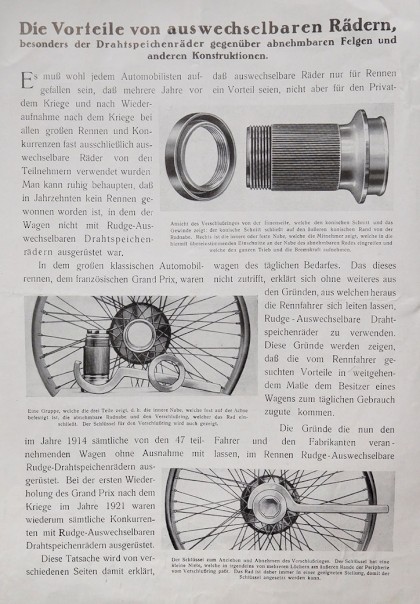
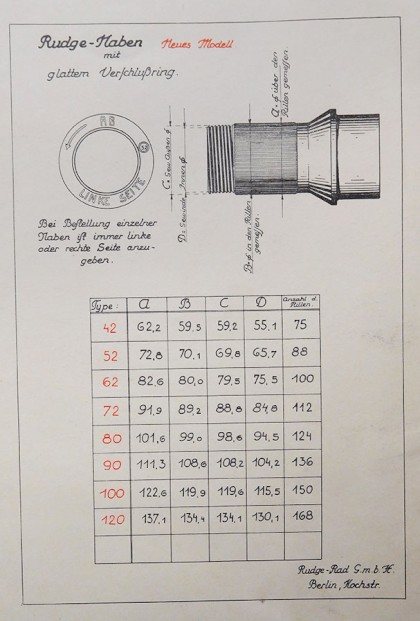
Centring
Centring a spoked wheel after the lacing is complete requires a lot of experience. Professional wheel makers here have decades of experience in order to have the correct, uniform tension in any situation. Crucial here are the minimum possible axial and radial run-out. Ideally, a dial gauge will read 0.1-0.2 mm of deviation from the zero point. Depending on the condition of the wheel, there can be much higher deviations. These might not necessarily influence the driving characteristics and functionality, however.
Cross number
The cross number for a spoked wheel is the crossing of two spokes on one level.
Cross spoke wheels
The cross spoke wheels represent a relatively new spoke wheel structure. Since the mid- 1980s, BMW had found a way to use tubeless spoke wheels. Here, the head of a straight pull spoke lies outside in the rim flange. The spoke nipple is installed on the hub side and has a Torx drive; this allows centring of the cross spoke wheel from the hub side – the classical spoke wrench is of no use here. This structure means that no air can escape through the dimpling/bore holes that are otherwise located in the centre. The term cross spoke wheel comes from the appearance of this structure. The spokes cross between the individual levels; this is not the case in a classical spoke wheel structure.
D
Dimples
Dimples are the circular bumps in the rim that were common during the middle and end of the 20s. The dimples were used to install the spokes at larger angles in order to achieve more stability. Before dimples were used, the hubs tended to have a smaller design, so as to have the most even surface possible where the nipple exits the rim.
E
Electromobility
The most diverse designs are finding increasingly popularity in society. Motors are built into the wheel as well as in the frames electric motorcycles and electric bicycles. Batteries are getting smaller and are being installed as close as possible to the motors. Stable spokes are a necessity because of the relatively high torque of electric motors.
Elongation at break A
The characteristic value for the extent of deformation of the sample.
H
History of the wheel
Spoke wheels were around as early as ancient Egypt, over 3000 years ago. As time went on, they gradually replaced disk wheels. The design of the first spoke wheels was such that the spokes were under pressure, unlike modern wheels. As a result the spoke had to very stable (today's alloy wheel). This changed at the end of the 19th century with the introduction of the tangential spokes. In this principle, the spokes are under tension. Since the material used is far more stable under tension than under pressure, this meant that lighter designs were possible. As a result, it was possible to make simple and more filigree spoked wheels.
Hook length
You can see the correct hook length on a tight spoke at the exit from the hub on the top of the hub (flange angle). The back head angle of the spoke must be as tight as possible in the hub.
Hole number
The number of holes in a spoked wheel differs significantly depending on the intended use. 28, 32, 36, 40, 48, 60, 72 and 84 hole are common hole numbers for spoked wheels.
L
Lacing
Lacing, by and large, is pure craftsmanship, apart from the assembly of the original. It generally takes place according to the specifications of the original. Special lacings in rebuilds with different rim sizes and widths can change significantly the spoke image. This is how the classic 40-hole Harley wheels are modified with 80-hole wheels, for example.
Logos
The logos of all well-known manufacturers of the spokes are mounted either on the spoke head or on the side below the spoke head.
M
Maintenance
The spoked wheel must be cleaned immediately in the event of contact with road salt or other aggressive materials. Use an appropriately gentle cleaning agent.
O
Offset
In terms of spoke wheels for cars, offset refers to the distance from the outer edge of the wheel to the wheel hub.
Offset
In the case of motorcycles, the offset is the distance from the rim to the hub. The question here is whether the wheel is built centred or off-centre to the hub (please measure before disassembly).
P
Pitch circle diameter
The pitch circle diameter for the hub is the distance from the spoke hole on one side to the spoke hole on the opposite side.
R
Radial angle
The radial angle on the spoked wheel identifies spoke progression from the wheel to the hub.
Recentring
The recentring of installed spokes is an absolute must with certain mileage, depending on the driving conditions. About 500-1000km is a guideline here. Please refer to the specifications of the vehicle manufacturer.
Reduction of area Z
During a tensile test a local reduction of area occurs after the tear strength is reached in ductile materials in the area where the break then takes place.
Rims
In the past, rims had different names. For example: old "WM3" – new "2.15"
Rim holes
As a rule of thumb, rim holes should be 0.5mm larger than the diameter of the nipple. Rim holes may be different. There are A rims and B rims, for example. The design is arranged so as to be mirrored; in this way, it determines if straight spokes or two sides of spokes will be installed. Special holes like those of car wheels or motorcycles like the BMW R50, Triumpf TT or Zündapp KS601 are possible.
Rim manufacturer
Rim manufacturers include, for example, Morad/Akront, Radelli, Excel, ERWE, Behr, SanRemo, TTS, D.I.D
Rim material
The rims material consists mostly of steel, stainless steel or aluminium.
Rim shapes
Flat shoulder rims, high shoulder rim, bead rims, wheel rims. A variety of contours within the shapes are possible, for example, MS, MT, or MTC rim types.
Rim size
The circumference of the wheels is measured on the rim.
Rim width
The rim width is the distance between two wheel rims and is measured in inches.
S
Spoke breakage
If individual spokes break, the entire wheel should be checked by a specialist workshop immediately. This usually indicates an imbalance in the spoked wheel that will manifest itself in additional spoke breakage. The spokes should be replaced immediately. The repair of the individual spokes does not solve the imbalance problem.
Spoke calculator
Spoke calculators on the Internet: When using the various spoke calculators, please bear in mind the uncertainty due to different dimples, hole diameters at the hub, etc.
- WWS Speichenrechner
- www.sapim.be/speichenrechner
- www.speichenrechner.de
- www.velo-classic.de/speich_rech.htm
Spoke dimensions
When it comes to the spoke dimensions, the bending angle and the hook angle play a decisive role in the durability of the spoked wheel, in addition to the material and workmanship.
Spoke heads
Spoke heads are provided by all manufacturers in a standard design with a 90° head angle.
Spoke length
The spoke length depends on the diameter of the hub, the diameter of the rim and the cross number.
Spoke levels
Spoke levels can vary depending on the intended use. Up to 6 levels are possible here. Two levels are used by default for motorcycles.
Spoke material
Stainless steel or steel grades are generally used. Titanium spokes are also available on the bicycle market.
Spoke shapes
There are many different spoke shapes: Smooth spokes, single butted spokes, double butted spokes, twisted spokes, conical spokes, bladed spokes.
Stability
The stability of a spoked wheel is a combination of the high-quality materials, the correct lacing (taking into account the correct spoke design) and the most uniform tension possible from centring.
T
Tensile strength Rm
Tensile strength is a material property: the maximum mechanical tension that the material can withstand before it breaks/tears.
Tie rod
Tie rods were and are used as special applications for all possible areas.

Tubeless
"Tubeless" is the technical name for tubeless tyres. TL tyres can be mounted with a tube. It is necessary to follow the manufacturer's instructions. Different contours are possible.
Tyres
Types of tyres are include diagonal tyres, diagonal belted, radial tyres with zero degree steel belt.
Tyre direction
The tyre direction must be observed.
Tyre load capacity
It is absolutely necessary to comply with the speed limits associated with the different designs.
Tyre sizes
Tyre size (inch to metric) can be determined in conversion tables.
Tyre storage
Tyres should be stored in a dark, dry and cool space with moderate ventilation.
Tyre tread
According to §36 Section 2 of the StVZO (German Road Vehicle Registration Regulations), tyre profiles must have a minimum tread depth of 1.6 mm. For bicycles with auxiliary engines, mopeds and light motorcycles, the minimum tread depth is 1.0 mm.
U
Uniform elongation A g
This is the plastic change in length during a tensile text, in relation to the initial measured length.
V
Valve
The installation of a new valve is recommended when installing a new tyre. In extreme cases, high centrifugal forces bend the valve significantly. Don't forget valve cap, it can prevent a pressure drop. Loosen the valve lock nut again after installation so that the valve can't break off.
W
Wheel lock
When spoked wheels first came into use, many different kinds of wheel locks were tried, e.g. those of the company Brevet SCAT.

Wire spoked wheels
Wire spoked wheels have been in use since the end of the 19th century for cars, planes, motorcycles, trikes, bicycles, tricycles and rickshaws. The term wire spoked wheels was created to distinguish these wheels from wooden spoke wheels, since revolutionized wheel building at the time.
Yield strength / proof strength Rp 0.2
The yield strength is an alternative to the yield point Re for different materials.
Measure
your spoke
online now.
With the new WWS spoke calculator.



























































































